Posted At: Jul 15, 2023 - 524 Views

What are the reasons to optimize MySQL tables?
The primary cause of an unoptimized MySQL table is the frequent execution of update and delete queries. As a result, fragmentation occurs, leading to the following consequences:
- The database table occupies more space than necessary.
- Retrieving data takes longer than optimal.
Techniques for optimizing MySQL tables involve organizing data within the database to eliminate redundant and unused space, resulting in efficient storage and improved query performance.
When Should You Optimize MySQL Tables?
Tables where information in a database continually updates, such as transactional databases, are the most likely candidates for optimization.
However, depending on the size of the database, the optimization query takes a long time to finish with larger tables. Therefore, locking a table for a long number of hours is not beneficial for transactional systems.
Instead of optimizing a table right away, consider trying some of these tricks for INNODB engine tables:
- Drop index, optimize, and add back index. If a table works without indexes for some time, dropping, optimizing, and adding back the indexes performs faster in some cases.
- Analyze which value benefits from compacting the most. Sometimes, the primary index is not useful or problematic. Optimizing for the wrong value causes fragmentation with secondary indexes.
Find Tables for Optimization
There are multiple ways to show tables and analyze them for optimization. Start by connecting to your MySQL database:
use <database name>
Depending on your use case, filter the information needed by following one of the tips below.
Tip 1: Show Unused Space in a Table
Check the status of the desired table with:
show table status like "<table name>" \G
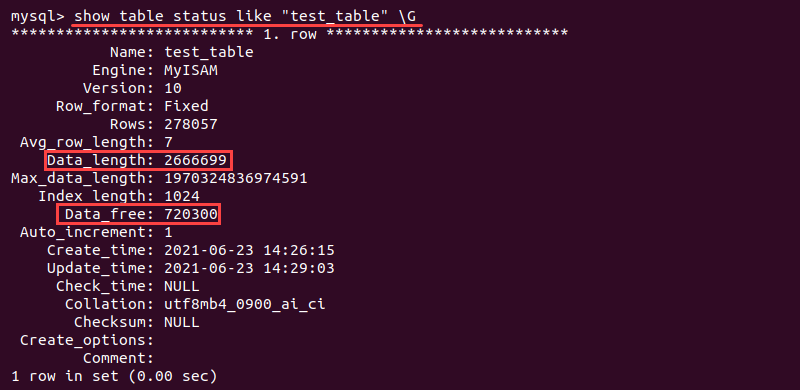
The output shows some general information about the table. The following two numbers are important:
- Data_length represents the amount of space the database takes up in total.
- Data_free shows the allocated unused bytes within the database table. This information helps identify which tables need optimization and how much space will be released afterward.
Tip 2: Show Unused Space for All Tables
The information schema stores metadata about a database schema. To check the allocated unused data for all tables in a selected schema, run:
select table_name, data_length, data_free
from information_schema.tables
where table_schema='<schema name>'
order by data_free desc;
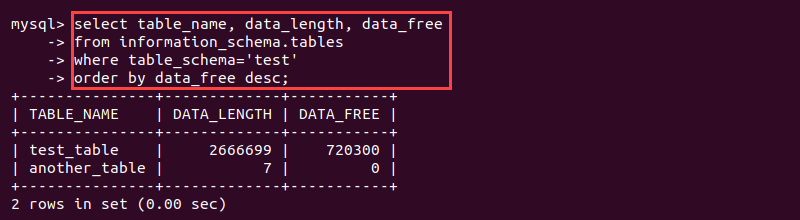
The query displays the name of the table, the total space, and unused allocated space. By default, the memory prints in bytes.
Tip 3: Display Data in Megabytes
Print the data in megabytes with:
select table_name, round(data_length/1024/1024), round(data_free/1024/1024)
from information_schema.tables
where table_schema='<schema name>'
order by data_free desc;
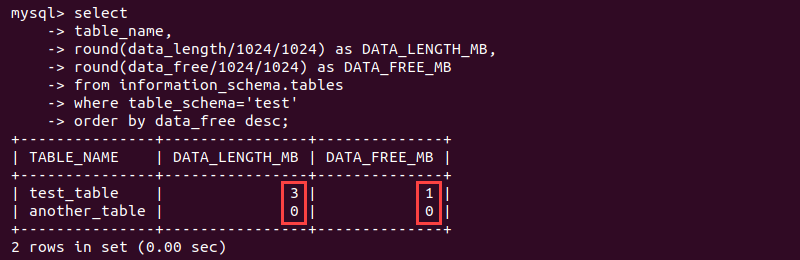
The example tables are not heavily fragmented. However, using optimize table helps free up some space from the test_table.
Optimize Tables
There are multiple ways to optimize tables by defragmentation. However, the general steps you perform are similar.
First, the process makes a temporary copy of the table where the optimization occurs. Then, when the operation finishes, the function replaces the original table with the optimized, renaming it after the original.
Tip 1: Optimize a Table Using MySQL
MySQL provides a function for optimizing a table. To optimize a table, use:
OPTIMIZE TABLE <table name>;
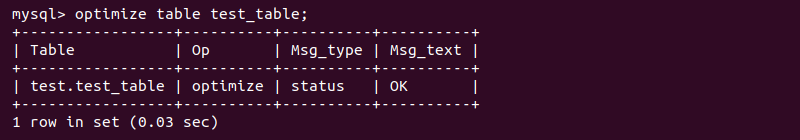
The output shows an informative status message about the actions and the results of the optimization in a tabular format.
Tip 2: Optimize Multiple Tables at Once
To optimize multiple tables at once, use:
OPTIMIZE TABLE <table 1>, <table 2>, <table 3>;
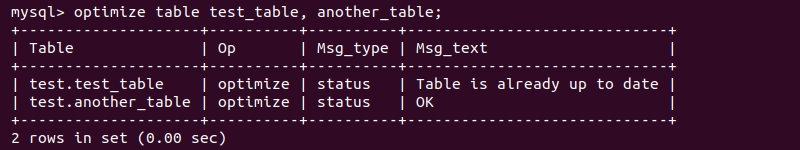
The result shows the status from the optimization for each optimized table.
Tip 3: Optimize Tables Using the Terminal
Perform table optimization through the Linux terminal with:
sudo mysqlcheck -o <schema> <table> -u <username> -p <password>
For example, to perform the check on a schema named test and table named test_table using the root user credentials, run:
sudo mysqlcheck -o test test_table -u root
To perform the optimization on multiple tables, separate each table name with a space:sudo mysqlcheck -o <schema> <table 1> <table 2> -u <username> -p <password>
After Optimization
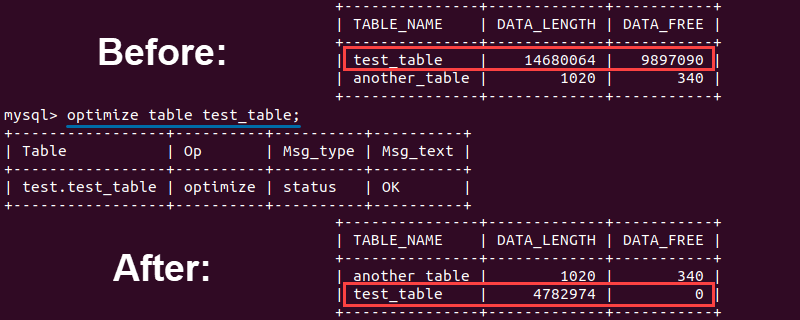
The results of the optimization change the values of data_length and data_free of the optimized table. Both values are lowered, indicating:
1. The optimization freed the unused allocated memory.
2. The overall memory of the database is lower because of the released space.
Conclusion
Optimizing MySQL tables requires careful consideration. This tutorial should help provide some practical guidance and tips on when to optimize MySQL tables.
